Dane's FAQs
Charpy testing, or impact testing was developed in 1905 by Georges Charpy in order to determine the amount of energy absorbed by a material during fracture. It was noticed that as the temperature drops, the tensile and yield of steel increases, but the ductility drops, leading to brittle and sometimes catastrophic failures. A standard Charpy... Read more
Per the RCSC section 16.2-12, multiple washers are permitted under the nut in order to resolve this problem.
Both are produced via the hot dip process, but with slightly different processing steps. G90 is a coating grade within the steel sheet specification ASTM A653, and is produced by uncoiling steel coils and running it at high speed through the pickling process and molten zinc before it passes through an air curtain, which creates... Read more
Proof strength, or proof load, is the full size equivalent of a yield test. Yield testing is typically only performed on machined specimens. In most fastener standards, full size testing is the preferred method, and the referee method if there is a discrepancy between the two test results. Because of the difficulty of getting reliable... Read more

There is no published requirement for making sure the ID marks are on the outside and visible. The main concern would be being able to ascertain that the proper nuts were installed. If all the ID markings are on the inside, they would not be visible, and an inspector could not see them. That said,... Read more
ASTM standards are typically called out by their ASTM number and year of revision, for example F1554-07. Occasionally, when small revisions are made at ASTM that do not necessitate a full year revision, the year is annotated with a letter. We fielded a chat recently where this question came up. Below is the correspondence and... Read more
There are many grades of nuts available in the marketplace, from your “run of the mill” nuts like you’d find at a hardware store, to specialized high strength structural nuts. These nuts are made from different materials and get their strength in different ways. Low strength nuts are made from a variety of materials and... Read more
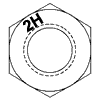
I have noticed in specifications from multiple organizations that ASTM A193 Grade B7 bolts are selected along with ASTM A194 Grade 2H nuts. I know that from ASME B16.5 Flanges and Flanged Fittings, the recommended high strength bolt is ASTM A193 Grade B7. However I cannot find in ASTM A193, A194, ASME B16.5, B18.2.1, B18.2.2, B31.1... Read more
A common misconception is that stainless steel is non-magnetic. There are five classes of stainless steel, and only one is non-magnetic. However, it just happens to be that the most widely used type (austenitic) is the one that is not magnetic. Class Magnetic? Common Types Ferritic Yes 430,442 Austenitic No 304,316 Martensitic Yes 410,416 Duplex... Read more
This is a common problem, and one that can be very difficult to remedy once the concrete is cured. As with most job-site fixes, the repair method depends on the nature of the problem and when in the construction process it is first noted. The repair method may be different if one bolt is out... Read more

