Newest FAQs
DFARS stands for Defense Federal Acquisition Regulation Supplement. This is a set of rules and restrictions that makes domestic or NATO materials preferred for United States defense contractors on military projects. A clause was added in 1973, amending the original regulation, currently allowing for materials to be melted in the following qualified countries per DFARS... Read more
Snug tight is defined by the AISC/RCSC as when all the plies in a connection have been pulled into firm contact by the bolts in the joint, and the bolts have been tightened sufficiently to prevent removal of the nuts without a wrench. They go onto say that this is typically achieved by a few... Read more
ASME, a global standards organization, provides dimensional guidelines and dimensional tolerances for a wide variety of fasteners and related items. Bent bolts, such as 90-degree bend anchor bolts, U-bolts, and eye bolts, fall under ASME B18.31.5. ASME B18.31.5 provides information regarding tolerances and quality, and their drawings also indicate where the bolts should be measured... Read more
Per ASME B1.1, threaded rods should be made at a 60 degree top angle. This is a standard that is produced throughout the United States, however, in recent years, Chinese manufacturers have figured out a way to save on steel costs by manufacturing threaded rods with 45 or 50 degree angles. This material does not... Read more
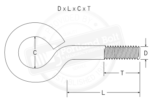
A tie rod assembly, used to brace steel columns, large timbers or canopies, often comes with clevises which are attached to mounting plates by a pin. These pins typically come in three configurations: headed pins with cotters, straight pins with cotters, and A325 structural bolts with a nut. Headed or ‘vertical’ pins possess a small... Read more

Most square nuts in the marketplace are made from low or medium carbon steel and are typically used with square head bolts. Their strength is not compatible with high strength bolts. These nuts are readily available in plain finish and hot-dip galvanized and are typically mass produced overseas. If you are looking for high strength... Read more

We run the nut onto the bolt until it stops, and we measure from end of inward face of the nut to end of bolt. This does not include any thread runout which can range from ½” long for ¾” diameter and 1-1/4” long for 2-1/2” diameter and larger.

The unthreaded portion of a headed bolt is called the grip. The length of all headed bolts (except countersunk head bolts) are measured from underneath the head to the end of the threads. The overall bolt length is made up of thread length plus grip length.
ASTM A193 Grades B8 and B8M Class 2 are grades of stainless steel bolts that are strain hardened and therefore have higher yield and tensile strengths than A193 Grades B8 and B8M Class 1 bolts. However, the ASTM A193 specification does not indicate a nut requirement used with Class 2 bolts, other than simply A194... Read more
There are many differences between these two specifications. In order to understand these dissimilarities there are overviews of each specification below followed by a short summary of these variances. For the purposes of this FAQ we will be focusing on A193 Grades B8 (Type 304) and B8M (Type 316) versus F593 Alloy Group 1 (Type... Read more
