Newest FAQs
For most tie rod assemblies that Portland Bolt provides, the clevises would be forged per ASTM A668 Class A, while the turnbuckles would be manufactured per ASTM F1145 class B. ASTM A668 is a general forging specification whereas F1145 covers turnbuckles specifically. If higher strength clevises are required to develop the strength of high strength... Read more

Supplementary requirements are optional requirements within ASTM specifications that must be requested at the time of quotation or purchase to be included, otherwise the manufacturing company is not required to adhere to the supplementary requirements. ASTM specifications have varying amounts of supplementary requirements. Some specifications have as many as six or more supplementary requirements, while... Read more

Yes, there is. A193 and A320 grades B8 and B8M are assumed to be Class 1 unless otherwise specified. Class 1 fasteners are carbide solution treated, while class 2 fasteners are carbide solution treated and strain hardened. The work hardening that occurs in the manufacturing of Class 2 fasteners increases their strength. Class 2 fasteners... Read more
Portland Bolt does not manufacture or supply bolts with a Class 3A thread. Instead, Portland Bolt manufactures and supplies bolts with a Class 2A thread and nuts with a Class 2B thread. The A designates a male thread and the B designates a female thread. Essentially there are three different classes of threads, the difference... Read more
Rotational capacity testing is a test “intended to evaluate the presence of lubricant, the efficiency of lubricant, and the compatibility of assemblies.” The test is intended primarily for galvanized fasteners and fasteners that must be fully tensioned in structural applications. With A325 bolts now falling under the new F3125 specification, which covers high strength structural... Read more

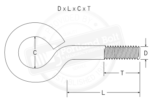
Portland Bolt manufactures eye bolts to pretty much any size imaginable. The type of eye bolt that Portland Bolt makes is not forged, but is turned and can be welded shut if needed. When load ratings are provided for eye bolts, they are normally for forged eye bolts, where the eye is formed as one solid... Read more
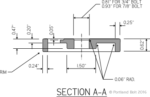
As the ASTM F3125 specification becomes more prevalent, the issue of configuration may be a source of confusion. The main reason is that in the past, ASTM A325 has been limited a heavy hex head structural bolt only, which implies a structural bolt thread length with Unified National Coarse thread. With the implementation of ASTM F3125, A325... Read more

It is often asked why some high strength hex nuts that are supplied with high strength bolts appear to be blue or some other color. This is normally the case with galvanized, high strength, heavy hex nuts and the reason for this is because of the wax lubricant applied to the nuts. According to the... Read more

The short answer is no. The A193 specification does not cover bolts larger than 1-1/2” in diameter for Class 2 materials. However, the reasoning behind this answer requires further explanation. Class 2 materials get their strength through the process of strain hardening (also known as work hardening or cold working). This process causes the grain structure... Read more
The physical dimensions of shear plates are governed by ASTM D5933. Shear plates come in two sizes, 2-5/8” outside diameter and 4” outside diameter. In several cases, we have been asked the dimensions of everything other than the OD and bolt hole. All of those dimensions are listed in the diagrams below. If your project requires... Read more